Introduction
In the IT services and consulting industry, success depends on continuous learning and the ability to translate technology into measurable business outcomes. With rapid advancements—AI adoption, multi-cloud strategies, DevOps, and cybersecurity—consultants need a structured framework for building skills and delivering value.
One surprisingly effective framework is Bloom’s Taxonomy, originally designed for education and research but extremely relevant for IT. It provides a progression model for consultants: from simply remembering technologies to creating innovative, client-specific solutions.
The Six Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy in IT Consulting
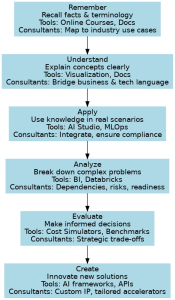
1. Remember – Building Foundational Knowledge
- Consulting Example: Learning the terminology of AI/ML (e.g., supervised vs. unsupervised learning, GPT models, data pipelines).
- Tool vs. Consultant: Tools like Coursera or Microsoft Learn support knowledge recall, but consultants map the knowledge to industry use cases (e.g., AI for customer service).
2. Understand – Explaining Technology Clearly
- Consulting Example: Explaining to a client what AI-powered chatbots can do and how they differ from traditional IVR systems.
- Tool vs. Consultant: Docs and visualizers help, but consultants bridge business & tech language for execs.
3. Apply – Executing Solutions
- Consulting Example: Deploying Azure OpenAI into an existing customer-support app.
- Tool vs. Consultant: Tools (Azure AI Studio, MLOps) help with deployment; consultants design workflows, integrate APIs, and ensure compliance (GDPR/HIPAA).
4. Analyze – Breaking Down Complex Problems
- Consulting Example: Deciding whether to prioritize predictive analytics, gen-AI, or automation first based on ROI.
- Tool vs. Consultant: BI/Datalake tools surface patterns; consultants analyze dependencies, risks, and readiness.
5. Evaluate – Making Strategic Recommendations
- Consulting Example: Recommending custom AI recommendations vs. off-the-shelf (e.g., AWS Personalize) for a retailer.
- Tool vs. Consultant: Tools benchmark cost/perf; consultants evaluate trade-offs in the client’s strategy & culture.
6. Create – Innovating for Clients
- Consulting Example: Designing a reusable AI accelerator (sentiment analysis + feedback loop + predictive sales) used across clients.
- Tool vs. Consultant: Tools (TensorFlow, Azure Cognitive Services, Hugging Face) are building blocks; consultants create tailored IP that differentiates.
Visual Guide – Bloom’s Taxonomy in IT Consulting
Why Bloom’s Taxonomy Matters in Consulting
- Structured Growth: Maturity path from junior (Remember/Understand) to architect (Evaluate/Create).
- Balanced Use of Tools: Shows where automation helps vs. where judgment is essential.
- Business Alignment: Higher levels ensure IT work drives transformation, not just code.
Conclusion
Tools can handle lower-order tasks—remembering, understanding, and applying. For higher-order work—analyzing, evaluating, and creating—consultants are indispensable. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to guide training and delivery helps teams deliver strategy, insight, and innovation—not just implementation.
